In the world of screens and displays, SVGA, XGA, and WXGA are terms that often pop up. These acronyms might sound technical, but they’re important factors to consider when selecting a monitor or DLP vs. LCD projector.
SVGA, which stands for Super Video Graphics Array, XGA, short for Extended Graphics Array, and WXGA, which stands for Widescreen Extended Graphics Array, all refer to different screen resolutions and formats. SVGA offers basic quality, XGA steps it up a notch, and WXGA introduces widescreen dimensions.
Choosing the right resolution matters because it affects the clarity and detail of what you see on screen. While SVGA might be suitable for simple tasks, XGA provides crisper images, and WXGA takes it a step further by offering a wider display. Your choice for ANSI Lumens vs. Lumens depends on how you plan to use the screen—whether it’s for work, entertainment, or a bit of both.
Let’s go in depth.
SVGA Resolution
SVGA, which stands for Super Video Graphics Array, refers to a standard screen resolution commonly used in older computer monitors and projectors. SVGA resolution played a significant role in shaping the visual quality of displays in the past which makes it the best daylight projector. Let’s delve into the details of SVGA resolution:
Historical Significance
SVGA was a significant improvement over its predecessors, offering increased screen resolution and better graphics capabilities.
Applications
SVGA resolution was widely used for a range of computing tasks, from word processing and basic graphics to early multimedia applications. It provided clear text and decent graphics quality for its time.
Resolution Details
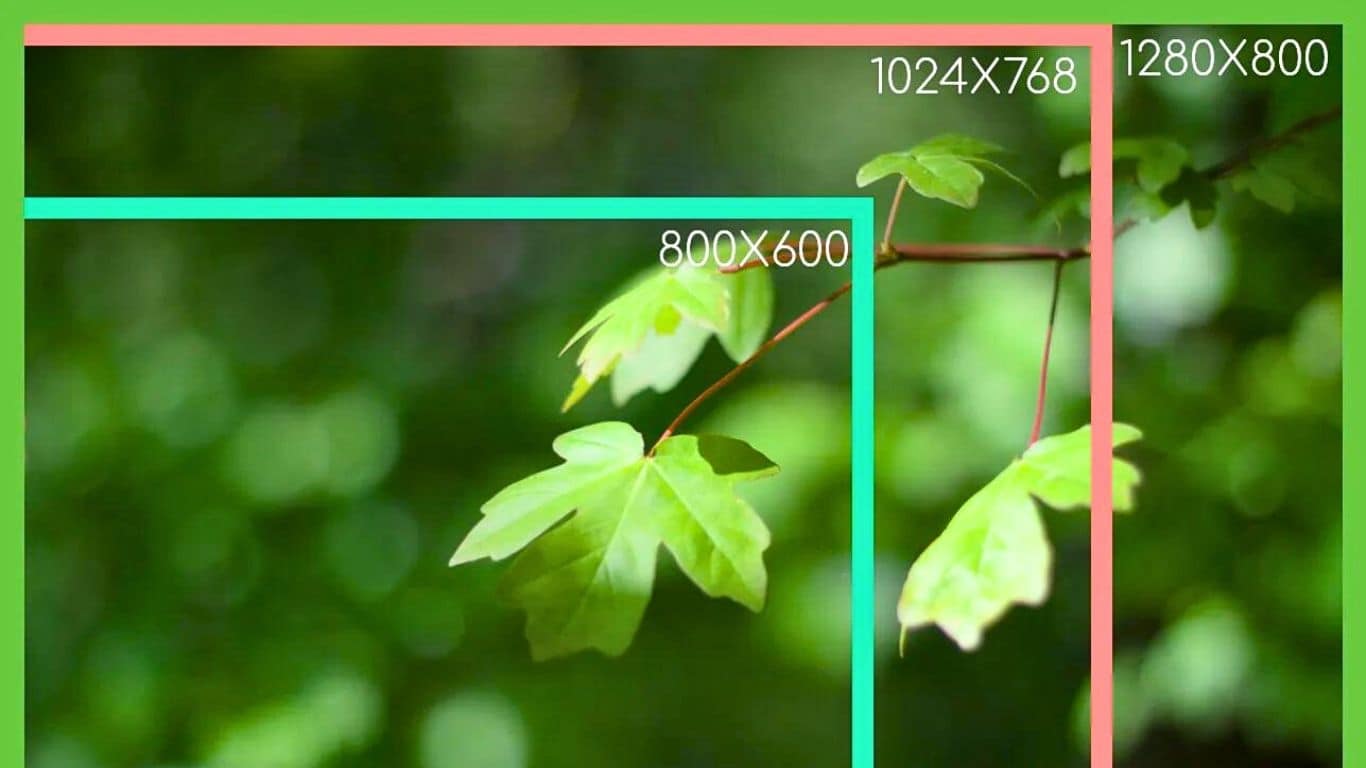
SVGA has a resolution of 800×600 pixels. This resolution defines the number of individual dots (pixels) that make up the images displayed on the screen. The pixel count in SVGA provides a balance between clarity and simplicity.


Aspect Ratio
SVGA adheres to the 4:3 aspect ratio, which was standard for many displays before widescreen formats became prevalent It helps to know what is contrast ratio is in a projector. This aspect ratio is more square-shaped compared to modern widescreen displays.
Evolution
As display technology advanced, resolutions higher than SVGA, such as XGA (1024×768) and beyond, became more common. These higher resolutions offered better detail and clarity, leading to improved visual experiences.
Modern Relevance
In contemporary settings, SVGA resolution is considered outdated for most computing and multimedia applications.
Legacy Systems
While SVGA resolution is not commonly used in modern devices, it may still find relevance in certain legacy systems, embedded applications, or specialized equipment where basic graphics capabilities are sufficient.
WXGA Vs WUXGA
When it comes to screen resolutions, the tech world loves its acronyms. Two commonly encountered terms are LUX vs. Lumens Projectors. While they might seem similar at first glance, they represent different levels of visual detail and clarity.
Let’s break down the distinctions between WXGA (Widescreen Extended Graphics Array) and WUXGA (Widescreen Ultra Extended Graphics Array) under various key aspects:
Resolution
- WXGA typically stands for a resolution of 1280×800 pixels.
- WUXGA takes things up a notch with a resolution of 1920×1200 pixels. This higher pixel count results in noticeably crisper images and greater detail. WUXGA is often found in larger monitors and projectors meant for professional use.
Clarity and Detail
- While WXGA provides satisfactory clarity for everyday tasks, it might not be sufficient for graphic-intensive work or media consumption due to its lower pixel density.
- WUXGA shines in terms of clarity.
Applications
- WXGA finds its niche in compact devices like laptops, tablets, and smaller monitors, where a balance between resolution and size matters.
- WUXGA’s enhanced resolution makes it ideal for larger displays for easy viewing, such as desktop monitors and projectors.
Work vs. Entertainment
This resolution works well for everyday tasks, web browsing, and streaming content, but might not deliver the immersive experience needed for high-definition media.
Cost Considerations
- Devices featuring WXGA screens often come at a more budget-friendly price point, making them accessible to a wider audience.
- WUXGA displays are associated with higher-end devices and professional equipment, which can translate to a higher cost.
WXGA vs. Full HD
In the realm of display technology, the terms “WXGA” and “Full HD” (also known as “1080p”) hold significant importance. These terms refer to distinct resolutions that impact the visual experience of screens, be it on laptops, monitors, or TVs. Let’s delve into the comparison to know how projectors work between WXGA (Widescreen Extended Graphics Array) and Full HD under various key categories:
Resolution
- WXGA boasts a resolution of 1280×800 pixels.
- Full HD is renowned for its resolution of 1920×1080 pixels. This higher pixel count translates to sharper picture elements, providing a crisper visual experience.
Clarity and Detail
- While WXGA delivers acceptable clarity for everyday tasks, its pixel density might fall short for graphics-intensive work and high-definition media consumption.
- Full HD excels in delivering superior clarity and detail. The increased pixel count ensures smoother lines, clearer text, and a more immersive viewing experience for videos and games.


Screen Size Considerations
- This resolution is often found in smaller devices like laptops and compact monitors, where maintaining a balance between projector screen size and resolution is crucial.
- Full HD is commonly seen in a wide range of devices.
Multimedia and Entertainment
- While WXGA suffices for standard web browsing and everyday tasks, it might not provide the full vibrancy and detail required for an optimal multimedia or gaming experience.
- Full HD shines when it comes to multimedia consumption. It offers the visual fidelity needed for enjoying high-definition videos, gaming, and visually demanding content.
Application Diversity
- Devices with WXGA screens are often chosen for affordability and portability with good projector screen material, making them suitable for students, casual users, and business professionals.
- Full HD appeals to a broader audience, catering to both entertainment enthusiasts and professionals who require accurate colors and fine detail.
Cost Considerations
- Devices featuring WXGA screens tend to be more budget-friendly, making them accessible for those seeking affordability without compromising usability.
- While Full HD devices might have a slightly higher price point, the enhanced visual experience they offer justifies the investment for many users.
XGA resolution Vs 720p
People get worried do projectors have a blue light. Let’s dive into the comparison between XGA resolution and 720p under various key aspects:
Resolution
- XGA boasts a resolution of 1024×768 pixels. This resolution provides a balanced display of images and text, suitable for various applications, from business presentations to general computing.
- 720p, also known as HD (High Definition), offers a resolution of 1280×720 pixels. While slightly lower in pixel count than XGA, it is specifically designed for high-definition content.
Clarity and Detail
- XGA delivers decent clarity for everyday tasks and presentations. However, due to its lower pixel count compared to 720p, it might not exhibit the same level of detail when it comes to fine lines and small text.
- 720p shines in terms of high-definition content. Its higher pixel count ensures sharper images and a more vibrant visual experience, making it ideal for watching HD videos and enjoying multimedia content which decides how long projectors last.


Multimedia and Gaming
- While XGA can handle basic multimedia content, it might not provide an immersive experience
- 720p excels in multimedia and gaming scenarios.
Aspect Ratio
- XGA typically follows a 4:3 aspect ratio, which is more common in older displays.
- 720p adheres to a 16:9 aspect ratio, which is the standard for modern widescreen displays and is well-suited for HD content.
Modern Relevance
- While XGA served well in its time, it’s now considered a lower resolution compared to modern standards, especially for media consumption.
- 720p remains relevant as a stepping stone into the world of high-definition visuals, although higher resolutions like 1080p (Full HD) and 4K have become more prevalent.
WXGA resolution Vs 1080p
In the world of screen resolutions, the terms “WXGA” and “1080p” stand out as defining factors for display quality.
These resolutions dictate the level of detail and clarity you’ll experience on your screen, Whether it’s a monitor, a TV, or a projector, you must know how to hang a projector screen. Let’s delve into the comparison between WXGA resolution and 1080p under various key aspects:
Resolution
- WXGA boasts a resolution of 1280×800 pixels. This resolution strikes a balance between screen real estate and clarity, making it suitable for compact displays and devices.
- 1080p, also known as Full HD, offers a resolution of 1920×1080 pixels. With a higher pixel count than WXGA, it delivers sharper images and more intricate detail.
Clarity and Detail
- While WXGA provides satisfactory clarity for everyday tasks, its pixel density might fall short for graphics-intensive work and high-definition media consumption.
- 1080p shines in delivering exceptional clarity and detail.


Multimedia and Gaming
- While WXGA suffices for standard web browsing and everyday tasks, it might not provide the full vibrancy and detail required for an optimal multimedia or gaming experience.
- 1080p excels in multimedia and gaming scenarios. It offers the visual fidelity needed for enjoying high-definition videos, gaming, and visually demanding content.
Application Diversity
- Devices with WXGA screens are often chosen for affordability and portability, making them suitable for students, casual users, and business professionals.
- 1080p appeals to a broader audience, catering to both entertainment enthusiasts and professionals who require accurate colors and fine detail.
Cost Considerations
- Devices featuring WXGA screens tend to be more budget-friendly, making them accessible for those seeking affordability without compromising usability, which depends on how many watts a projector uses.
- While 1080p devices might have a slightly higher price point, the enhanced visual experience they offer justifies the investment for many users.
SVGA Vs XGA Vs WXGA – FAQs
Conclusion
This article consists of professional research and personal experiments to help you choose the right resolution for your display needs depending on what you want to do.
SVGA is basic and budget-friendly, suitable for simple tasks. XGA offers improved clarity but still lacks detail for high-def content. Meanwhile, WXGA brings widescreen clarity and versatility for presentations and entertainment which makes it the best projector under $300.
If you need crisp visuals and better text, WXGA is a good choice. Each has its place, with SVGA being the simplest, XGA bridging the gap, and WXGA offering a balanced experience. Consider your usage, budget, and the visual experience you want to make the best decision.

